 advertisements advertisements
|

|
NASA sends historic Apollo mission control consoles to be restored
Jan. 25, 2018 — The historic consoles used by NASA flight controllers to manage the first missions to land astronauts on the moon are on the move.
Workers on Thursday (Jan. 25) were busy labeling and removing the iconic rows of consoles that comprised NASA's historic mission control at the Johnson Space Center in Houston. The green metal cabinets, with their cathode-ray tube displays, rotary dials and backlit push button panels, are being temporarily relocated to the Cosmosphere museum in Hutchinson, Kansas, where they will be restored to their Apollo-era condition and appearance.
"All of these historical consoles have been catalogued and we are removing them from the room and sending them to our restoration contractor," said Jim Thornton, NASA's project manager for the restoration, during a media tour Thursday. "This is [the first] stepping stone in the overall project to restore the original Apollo flight control room, visitor viewing room and the simulation control room back to the way they appeared in July of 1969."
The $5 million restoration will return Mission Operations Control Room-2 (MOCR-2) inside the Mission Control Center to how it looked at the time of Apollo 11, the first mission to land humans on the moon.
"This will be a complete and accurate historical restoration," said Sandra Tetley, the historic preservation officer and real property officer at Johnson Space Center. "It will not be a fix-it-up. Everything will be preserved and accurate, from buttons, button labels, lighting — everything will be completely accurate."
"It's going to look as if the flight controllers just walked out of the room," she said.
Space Center Houston, the visitor center for Johnson Space Center, together with NASA, Texas Historical Commission and the National Park Service are overseeing the project, with the goal of it having ready in time for the 50th anniversary of the first lunar landing next year. The Park Service gave its approval for the restoration in 2017 given the room's status as a National Historic Landmark since 1985.
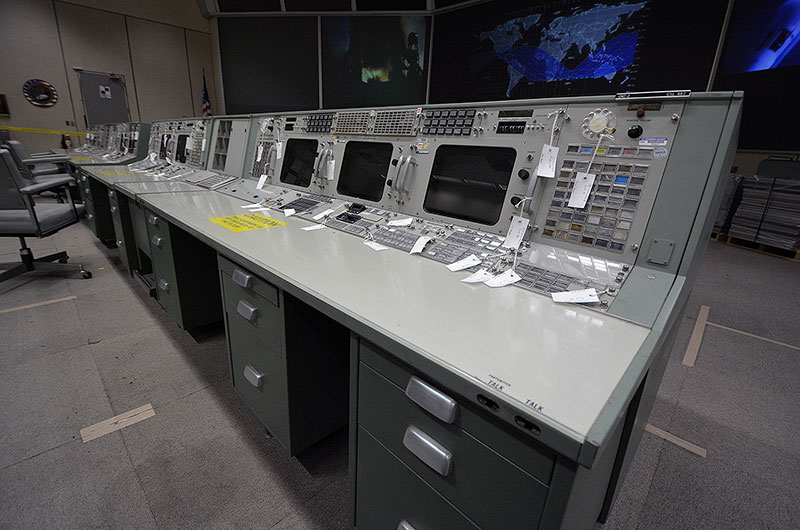
Before removing the consoles, each component needed to be tagged and entered into a database.
"Every piece that goes out has to be documented," Tetley told collectSPACE. "We went through and documented every part and serial number, manufacturer's part number and which console and which position it is in."
Though the overall control room is being returned to its Apollo 11 appearance, the consoles will be configured to how they looked during the fourth moon landing in July 1971. The Apollo 15 mission included the first use of the lunar roving vehicle (lunar rover) and began the extended exploration of the moon.
"The flight controllers said Apollo 15 was the height of the technological changes in the Apollo program. After that mission, the console configuration did not change very much," Tetley said.
At the Cosmosphere's SpaceWorks restoration facility, conservators will carefully take apart the more than half-century old consoles in order to bring them back to life.
First used for NASA's Gemini 4 mission in 1965 and retired after STS-53, the 52nd space shuttle mission in December 1992, the consoles' electronics are largely no longer serviceable. As such, the displays and some of the other visible elements will be augmented with modern components in order to create the appearance that the consoles are operational.
"We're not re-energizing the consoles, but they will animated to appear as if they are," said Thornton.
"They will be representative working," added Tetley. "They will be backlit with LED lighting so the visitor's experience is such that when you are in the viewing room looking in, all of the lights and monitors will be the same as when we were landing on the moon."
First to depart by truck for the Cosmosphere are the consoles from the simulation control room and the first two rows of the main room — including the stations for the retrofire officer (RETRO), flight dynamics officer (FDO), capsule communicator (CAPCOM) and electrical, environmental and communications officer (EECOM). They are slated to return to Houston in October, when the second and last set of consoles, including the flight director (FLIGHT) station, is expected to leave.
In the meantime, work to restore the rooms themselves is beginning, with details like the carpet, ceiling tiles, wallpaper and upholstery being cleaned or replaced to match their 1969 appearance. |
|
 |

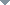
Inside Mission Operations Control Room-2 (MOCR-2, also known as Flight Control Room-2 or FCR-2, or Historic Mission Control), workers have prepared the Apollo-era consoles for being moved to the Cosmosphere in Hutchinson, Kansas by inventorying and tagging every part and component by serial number and console position. (collectSPACE) |
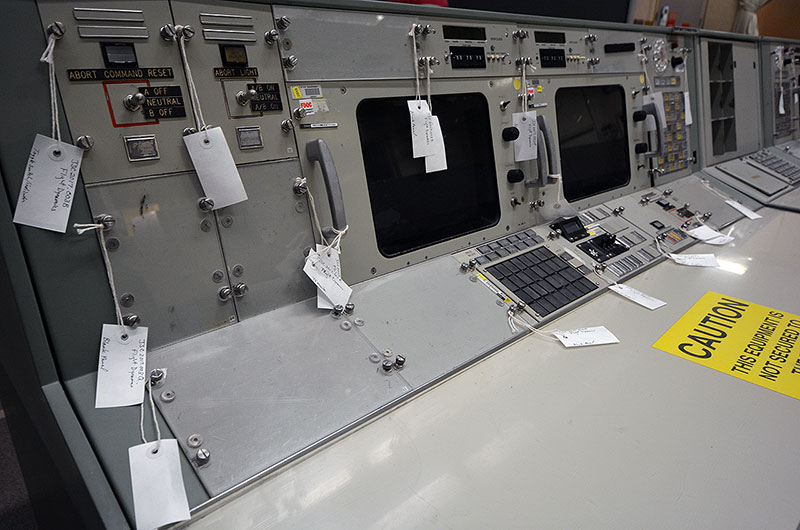


"Everything that happens to it, where it goes, what's done to it has to all be documented." — Sandra Tetley, historic preservation officer at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston. (Pictured: Cosmosphere curator Shannon Whetzel tagging a component.) (collectSPACE) |
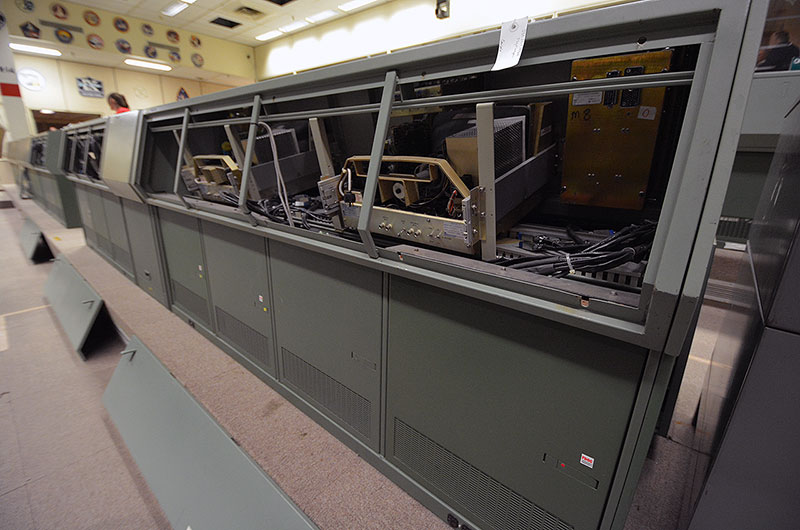

The Cosmosphere will preserve the original electronics inside the consoles, but will also install modern technology to give the appearance that the consoles are again active, monitoring the first landing on the moon. (collectSPACE) |
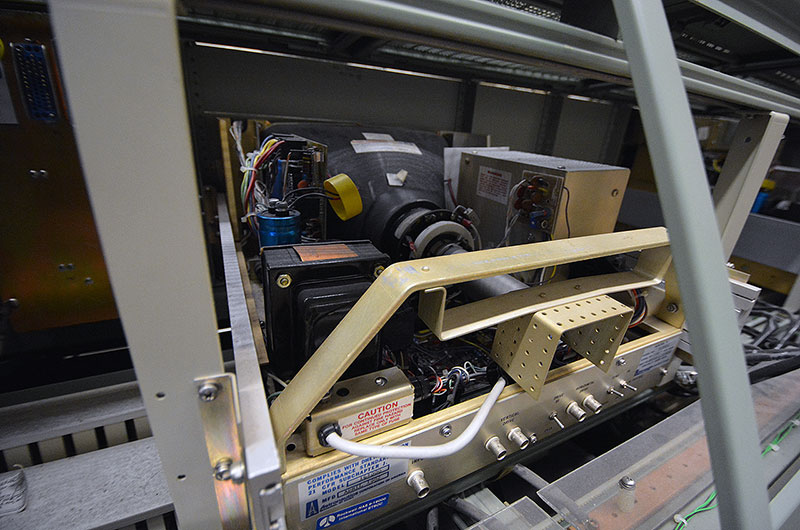
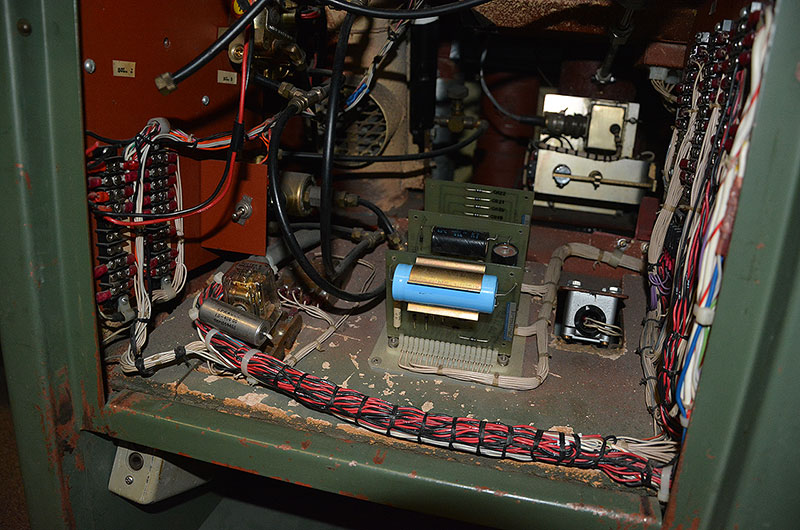
The Cosmosphere's SpaceWorks division conservators will work to arrest corrosion and reverse damage to the consoles. (collectSPACE) |
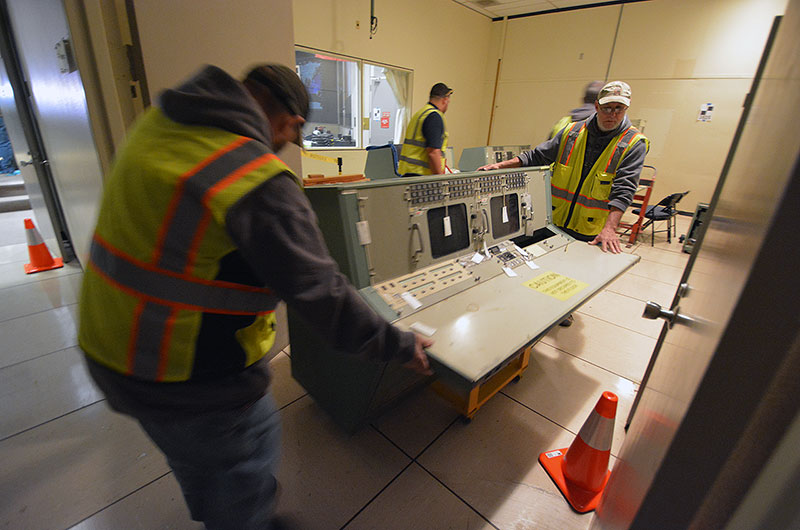

Cosmosphere and NASA workers remove a console from the simulation control room for its delivery to the Kansas museum. (collectSPACE) |
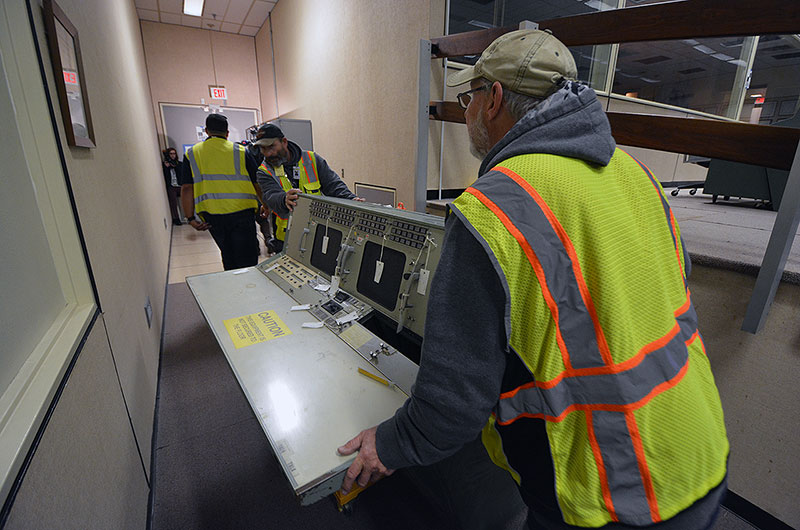
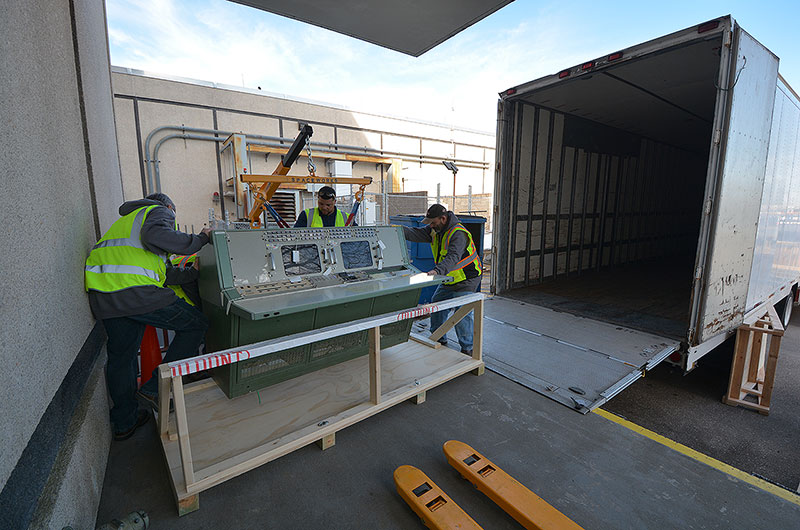


The consoles were loaded onto pallets, wrapped in padding and loaded on a truck bound for the Cosmosphere in Kansas. (collectSPACE) |
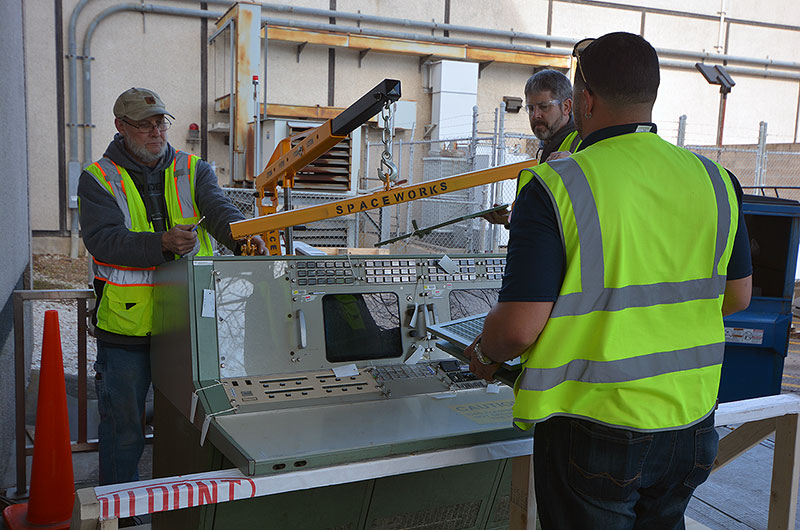
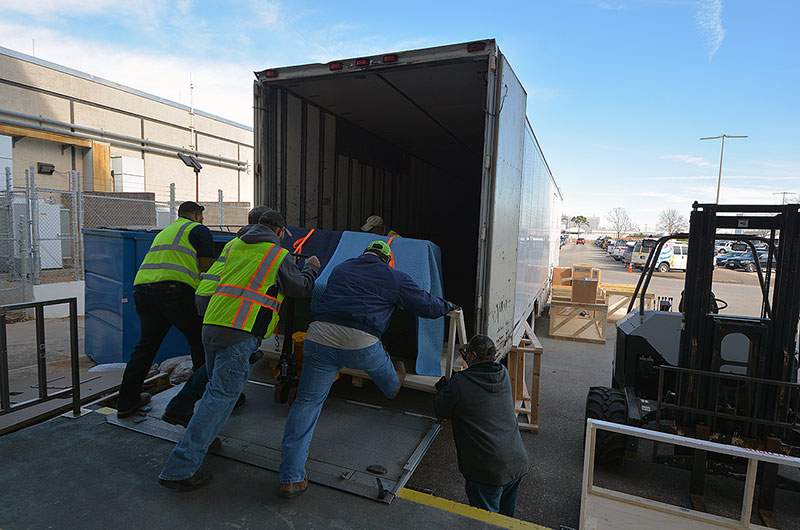



|

© 1999-2025 collectSPACE. All rights reserved.
|
|

|

|
