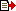
A United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta IV rocket successfully launched the AFSPC-4 mission for the U.S. Air Force on July 28 at 7:28 p.m. EDT from Space Launch Complex-37. This is ULA's eighth launch in 2014, and the 85th successful launch since the company was formed in December 2006.
"The ULA team is proud to have delivered the twin Geosynchronous Space Situational Awareness Program (GSSAP) spacecraft to orbit today," said Jim Sponnick, ULA vice president, Atlas and Delta Programs. "We are privileged to work with a top notch U.S. government and contractor mission team that is committed to mission success."
This mission was launched aboard a Delta IV Medium-plus (4,2) configuration Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle (EELV) using a single ULA common booster core powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-68 main engine, along with two ATK GEM-60 solid rocket motors. The upper stage was powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RL10B-2 engine, with the satellite encapsulated in a 4-meter-diameter composite payload fairing.
In addition to the two GSSAP satellites delivered to near-geosynchronous orbit, the secondary payload, Automated Navigation and Guidance Experiment for Local Space (ANGELS) satellite is managed by the Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL).

"This launch marks the first EELV secondary payload adapter (ESPA) to launch on a Delta rocket," said Sponnick. "This mission represents an excellent utilization of rideshare capabilities that has enabled a low-cost way for the AFRL ANGELS team to flight demonstrate future spacecraft technologies."
The twin GSSAP spacecraft will support U.S. Strategic Command space surveillance operations as a dedicated Space Surveillance Network sensor. The GSSAP will also support Joint Functional Component Command for Space to collect space situational awareness data, allowing for more accurate tracking and characterization of man-made orbiting objects. ANGELS examines techniques for providing a clearer picture of the environment surrounding our nation's vital space assets.