Several rare herbal plants aboard the recent Shenzhou-7 space mission have now been transferred to a Chinese nanobiotechnology lab for study.The plants, including rauwolfia and salvia miltiorrhiza (also known as red sage), were used to produce nanomedicines to treat cancerous tumors, Professor Zhang Yangde with China's Laboratory of Nanobiotechnology at the Central South University told the Changsha Daily newspaper in Hunnan Province on Thursday.
Chinese scientists on Sunday successfully directed the accompanying satellite BX-1 to begin circling the Shenzhou-7 spaceship, on an elliptical track of 4 kilometers multiplying 8 kilometers.It is the first time that China has succeeded in maneuvering this kind of space orbiting, official sources say.
The accompanying satellite began orbiting the orbital capsule of the Shenzhou-7 at 18:14 pm, under the close monitoring and precise control of the Beijing Aerospace Control Center.
The BX-1 rode the Shenzhou-7 into the space on September 25 and it was launched by the spacecraft two days later. Since September 30, the control center changed its track six times to draw it closer to the space vehicle step by step, and finally it succeeded in orbiting the capsule.
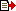
Over the past days, the monitoring satellite has shot over 1,000 pictures of the spaceship from different angles. All the pictures are clear and complete, said an official with the space program.
The photos were condensed and stored after they were taken by the cameras installed on the satellite. The BX-1 shot its first photo six seconds after being released.
In one of the pictures published by the official, the spacecraft was flying like an eagle with the Earth as its background.